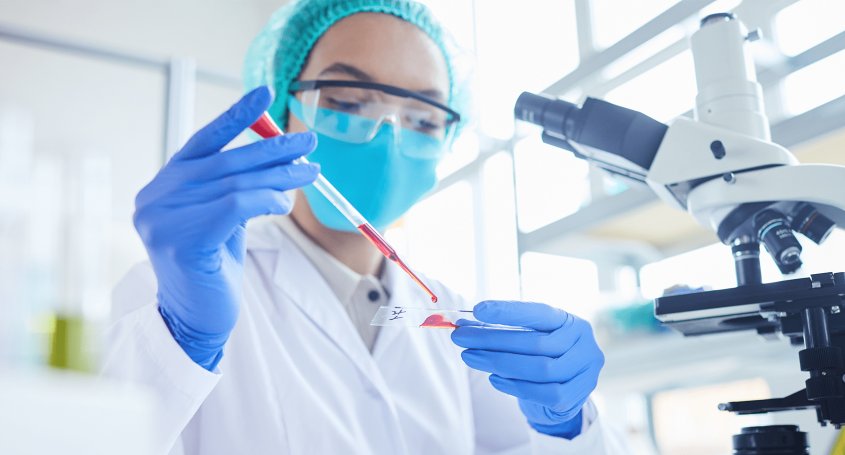
After the good news of a pregnancy, parents are also concerned about the baby's health. Prenatal tests such as the non-invasive prenatal test and amniocentesis help to diagnose possible anomalies through DNA, such as spina bifida due to neural tube defects, hereditary metabolic diseases or genetic malformations, in order to monitor the wellbeing of the foetus.
Until relatively recently, it was only possible to detect these abnormalities through amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. Today, however, a simple maternal blood test can detect chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus, the best known of which is Down's syndrome. This test thus offers an alternative to invasive techniques, which, although effective, always carry a 1% risk of miscarriage.
Non-invasive prenatal testing, what does it consist of?
It is a non-invasive diagnostic test that is performed from the 10th week of pregnancy through an analysis of maternal blood. The blood sample is used to look for foetal cells that have accidentally passed from the foetus into the mother's blood. These cells will be used to rule out abnormalities in the most important chromosomes, including 21 - which implies Down's syndrome, 18 - Edwards' syndrome, and 13 - Patau's syndrome.
Non-invasive prenatal testing is especially recommended in:
- Women in whom suspicious alterations have been detected in ultrasound scans or triple screening.
- Women with previous pregnancies with Down syndrome
- Couples in which both partners are carriers of autosomal recessive diseases
- When one of the parents is a carrier of a karyotype abnormality
Its reliability is over 97%. If the test result is negative, amniocentesis is completely excluded as the possibility of Down's Syndrome, other trisomies and alterations in the sexual chromosomes are ruled out with a very high degree of certainty.
If the test is positive, an amniocentesis is necessary to confirm the result. The risk of false positives, i.e. that the test says that there is a chromosomal abnormality when in fact there is not, is 0.1%. The possibility of having a chromosomal alteration is very high, but not high enough to make decisions about the future of this pregnancy.
Amniocentesis, what does it consist of?
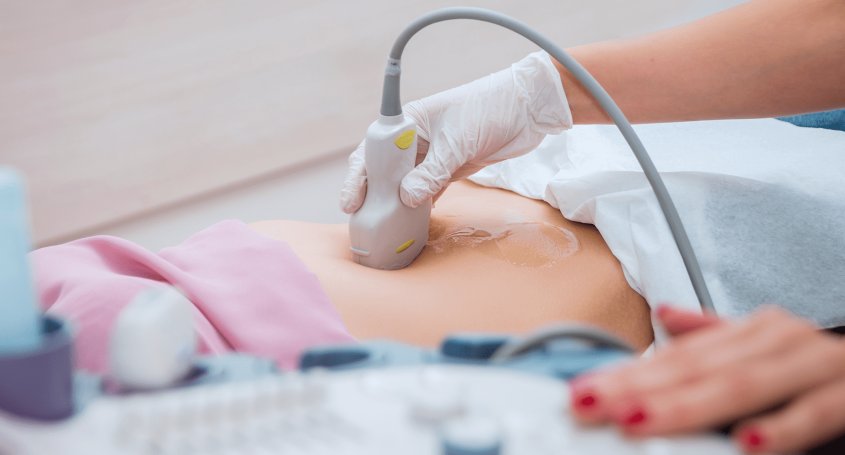
Amniocentesis is one of the most worrying tests during pregnancy. It consists of introducing a fine needle into the amniotic sac through the mother's abdominal wall. The main objective is to obtain the foetal cells floating in the amniotic fluid in order to carry out genetic studies. It is most commonly performed at around 14-16 weeks.
It is a short ambulatory procedure that does not require any medication. The test consists of an ultrasound scan to locate the amniotic fluid and a puncture of the patient's abdomen through a fine needle. Thanks to the ultrasound, the needle advances towards the amniotic fluid sac, always monitoring the movement of the foetus. A small amount of fluid is withdrawn depending on the tests to be performed, normally 5-10 millilitres, and the needle is removed. The chromosomes are analysed through this fluid extraction.
Although it is a very safe test, complications can occur and can lead to miscarriage in 1% of cases.
Therefore, in the short term, a reduction in the number of amniocenteses to be performed is expected, as the indication for this invasive test will be limited to a small number of cases in which the test has altered results.