What genetic information can we get from the embryos?
Depending on the indication, the following genetic tests can be performed:
Aneuploidy test
This test consists of examining the number of chromosomes in the embryo by applying NGS.
The transfer of embryos with genetic abnormalities may decrease the pregnancy rate and increase the percentage of miscarriages. Identifying these embryos improves the success rates in an assisted reproduction programme. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is recommended in those cases in which there is a chromosomal risk for the embryo, such as:
- Couples with recurrent miscarriages
- Women of advanced reproductive age
- Implantation failures
- Genetic male factor
Structural chromosome abnormalities
Occasionally we find healthy patients with abnormalities on their karyotype who only have problems when trying to achieve a pregnancy. Those patients who are carriers of balanced or Robertsonian translocations, as well as inversions, may generate abnormal embryos. In these cases, the Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) technique is recommended to identify the altered embryos and avoid their transfer.
Monogenic diseases
Another type of abnormality are those that are caused by a single gene mutation. These abnormalities are not identifiable with karyotype and the specific DNA structure needs to be examined in order to identify them.
Transmission of certain genetic diseases through the parents can be avoided by applying Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) on the embryos collected during an assisted reproduction cycle. A few of these diseases are cystic fibrosis, beta thalassaemia or some muscle dystrophies.
How is Preimplantation genetic diagnosis performed?
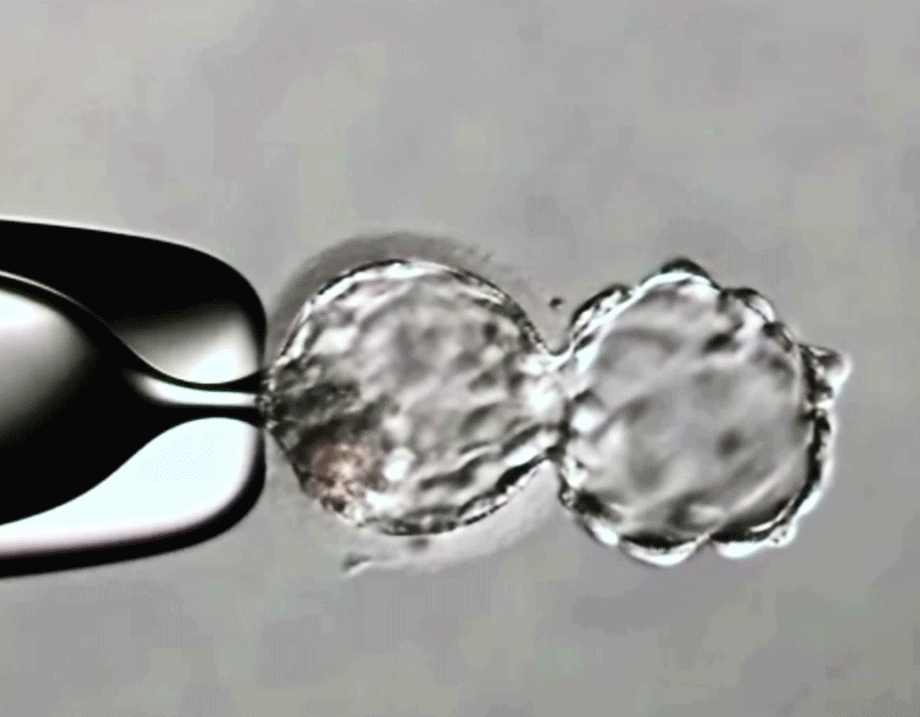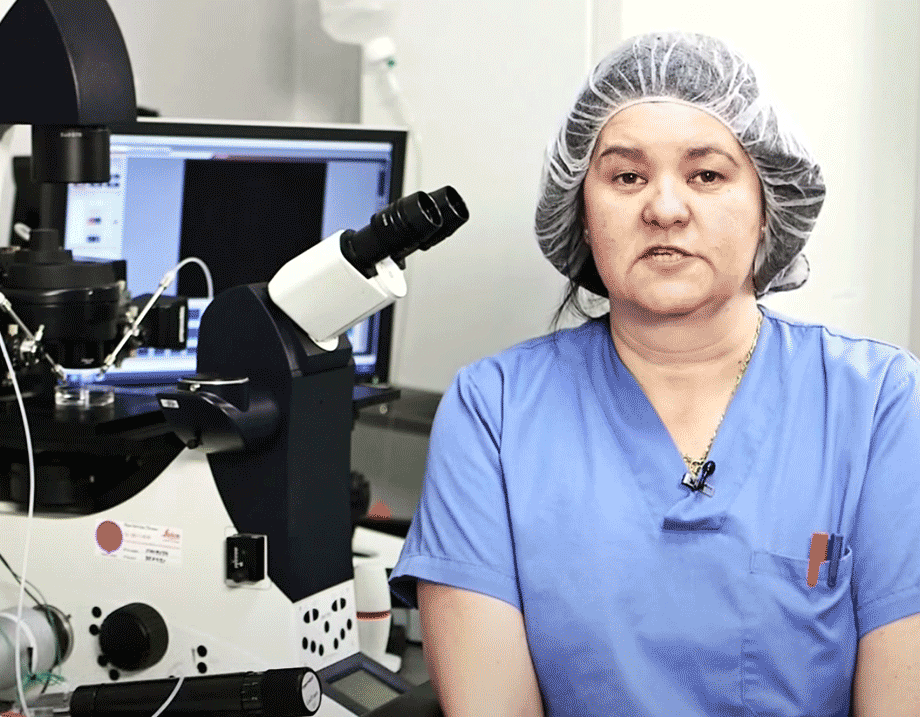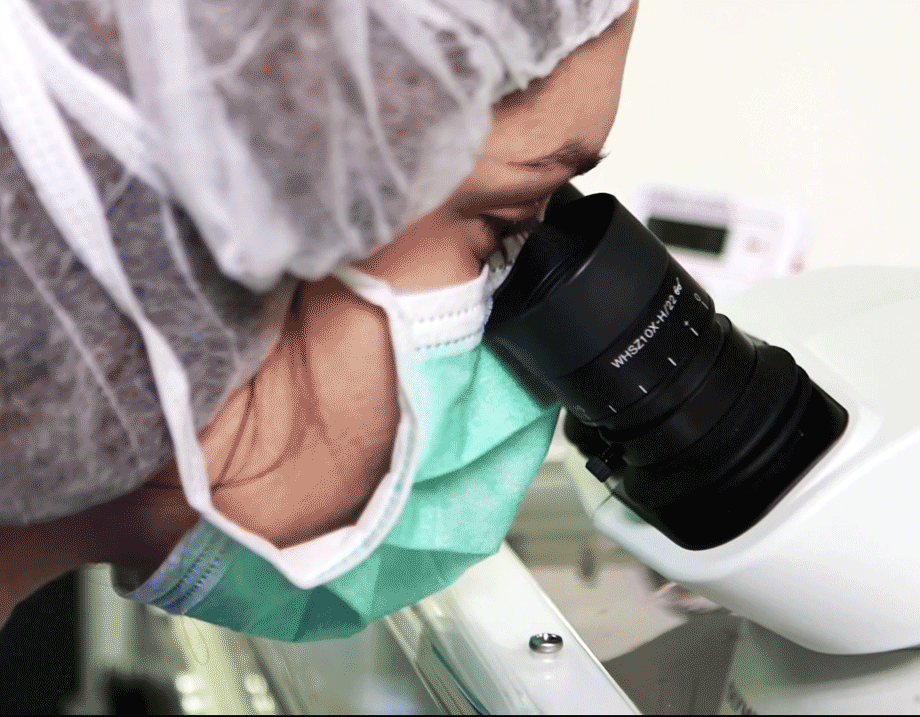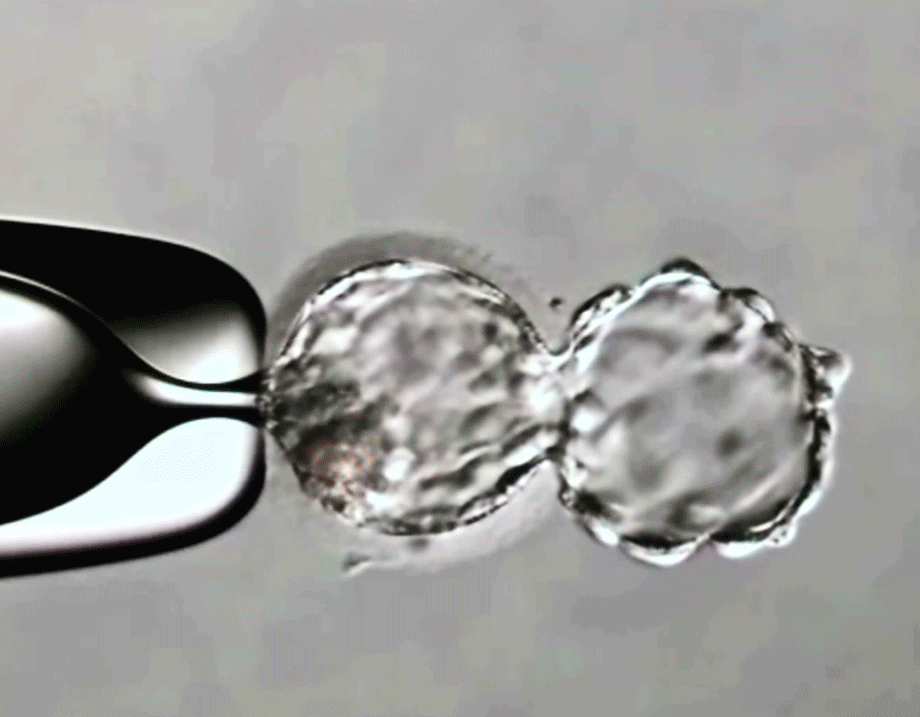
How are the embryo cells collected?
Embryo biopsy is performed when the blastocyst stage is reached on day 5-6 of its development.
In order to perform the biopsy, a laser is used to drill a hole into the zona pellucida of the embryo, through which trophectoderm cells are collected for examination.
When are the examined embryos transferred?
The trophectoderm biopsy is performed on day 5-6 of embryo development. The genetic test results will be available within a few days, therefore the embryos should be frozen after the biopsy. Once we have the genetic results, the cycle for transferring normal embryos can be organised.
Can the embryos be frozen after PGD?
Yes, through the vitrification technique, we can freeze all the embryos without them undergoing any kind of damage.