I am not getting pregnant.
What should I do?
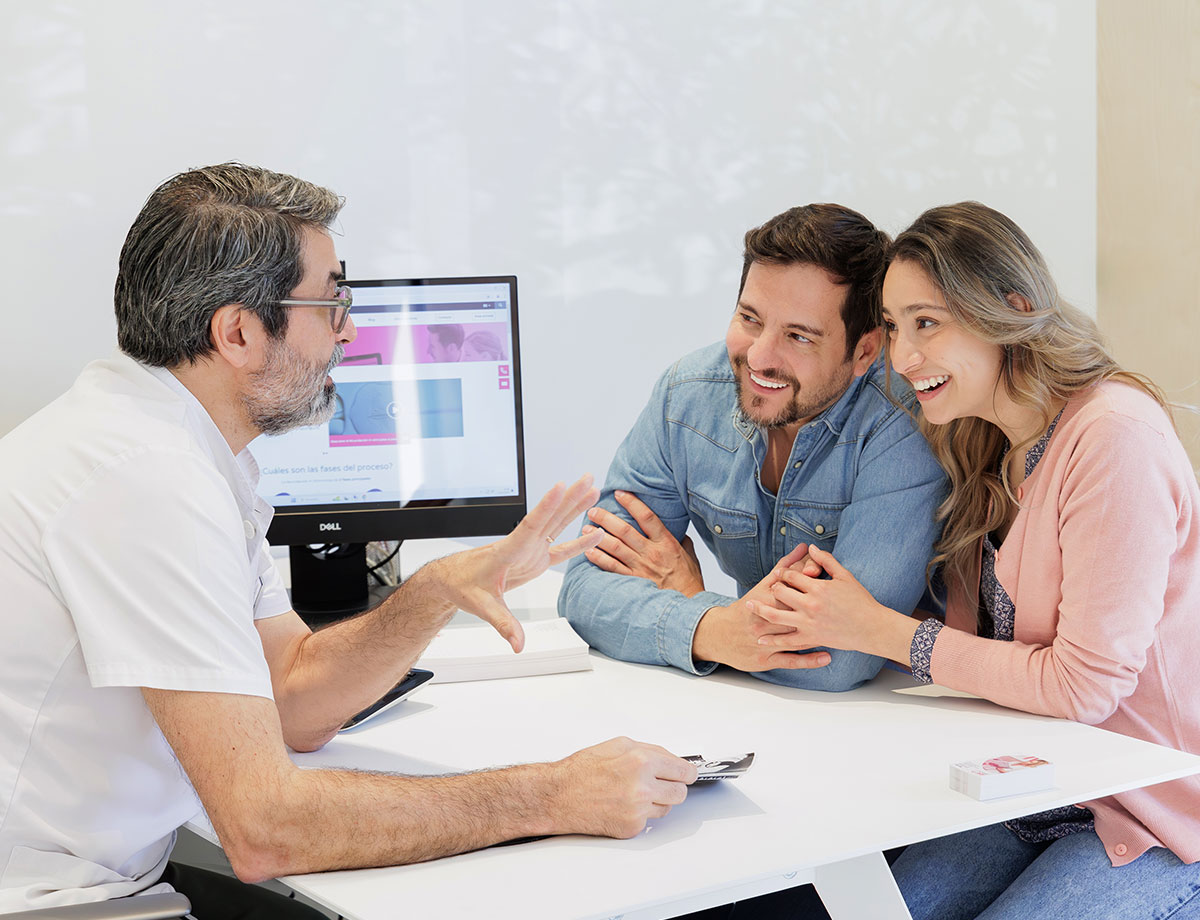
Achieving a pregnancy is not always easy and several months can pass to achieve it. When trying to become pregnant takes more than one year, something might not be working as it should be and a basic sterility evaluation is recommended to determine the cause.
There are situations where it is recommended to have a sterility consultation after no more than six months:
Women aged ≥38
Irregular cycles of more than 35 days
Previous ovarian surgery
Diseases like endometriosis
Previous treatments with chemotherapy
Two or more consecutive miscarriages