Sexual intercourse should always be a pleasurable experience. However, many women experience pain during intercourse, a situation that affects both their physical and emotional well-being, as well as their relationship.
What is dyspareunia and what are its symptoms?
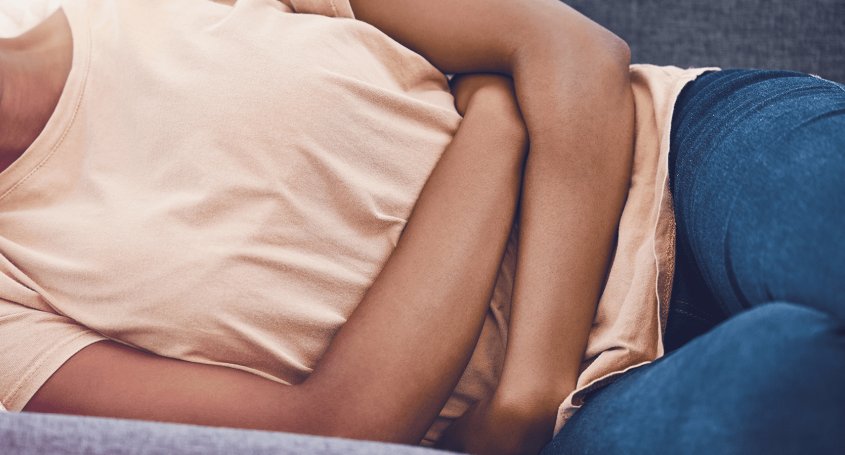
Dyspareunia is not a disease in itself, but a symptom that can be related to multiple causes. It is defined as persistent or recurrent genital pain associated with sexual intercourse. This pain can occur before, during, or after intercourse and, in some cases, can be incapacitating.
In addition to pain, dyspareunia can manifest as burning, stinging, or involuntary spasms of the vaginal muscles.
Depending on the location of the pain, we distinguish between two main types:
- Superficial dyspareunia: occurs at the beginning of penetration, at the entrance to the vagina.
- Deep dyspareunia: occurs during penetration and can extend to the pelvis or abdomen.
Causes of dyspareunia :
There are many causes that can lead to dyspareunia, which is often a multifactorial symptom. Generally, the causes fall into three categories: physical, hormonal, or emotional.
Physical causes:
- Vaginal or urinary tract infections (candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, cystitis).
- Vaginal dryness, common during menopause or breastfeeding.
- Endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Pelvic floor disorders, such as vaginismus.
- Scarring from episiotomies or pelvic surgery.
- Anatomical malformations or vaginal stenosis.
Hormonal causes:
- Estrogen deficiency, common during menopause, postpartum, or resulting from the use of certain contraceptives.
- Endocrine disorders that affect vaginal lubrication and elasticity.
Emotional or psychological causes:
- Anxiety, fear of pain, or traumatic sexual experiences.
- Relationship problems, low self-esteem, or lack of sexual desire.
How is dyspareunia treated?
Treatment depends on the cause, so a comprehensive medical evaluation is essential. This should include a medical history, physical examination, and, if necessary, additional tests such as hormone tests, cultures, or ultrasounds.
Therapeutic strategies may include:
- Vaginal lubricants, especially useful in cases of dryness.
- Local hormone therapy with estrogen, if there is vaginal atrophy.
- Antimicrobial treatment (antibiotics or antifungals) if there is an infection.
- Anti-inflammatories or pain relievers.
In addition, pelvic floor physical therapy plays a key role in many cases.
Relaxation techniques, muscle re-education, or the use of dilators can help improve elasticity and reduce pain.
When emotional factors are involved, it is advisable to seek individual or couples therapy with professionals specializing in sexual health.
Don't normalize pain: seek help.
If you experience recurrent pain during sexual intercourse, don't normalize it or ignore it. Many women take years to seek help due to embarrassment, ignorance, or fear, but dyspareunia can be treated.
A personalized, empathetic, and multidisciplinary approach is the key to regaining a satisfying and pain-free sex life.
Dr. Cristina Guix
Gynecologist specializing in fertility at Barcelona IVF