Hyperandrogenism is a medical condition characterized by the presence of elevated levels of androgens or male sex hormones in women.
What are its causes?
The most common cause of hyperandrogenism is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). However, it can also be associated with other conditions, such as:
- Adrenal gland disorders, such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia or adrenal tumors.
- Use of certain drugs, such as anabolic steroids.
- Obesity, which can aggravate insulin resistance and promote excess androgens.
What symptoms do women with hyperandrogenism have?
This hormonal imbalance can trigger several symptoms:
- Hirsutism: presence of hair in typically male areas, such as the face, chest and back.
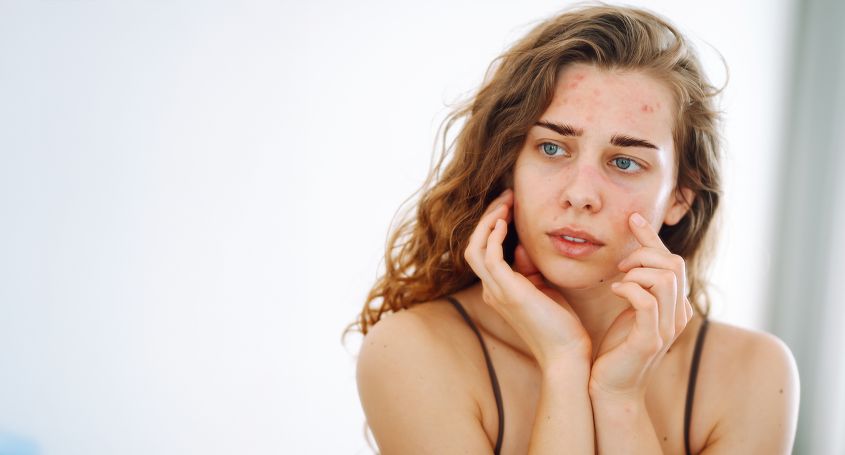
- Severe acne and oily skin: due to increased activity of the sebaceous glands.
- Menstrual alterations: such as amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) or irregular cycles, which can generate fertility problems.
- Androgenetic alopecia.
Treatment of hyperandrogenism
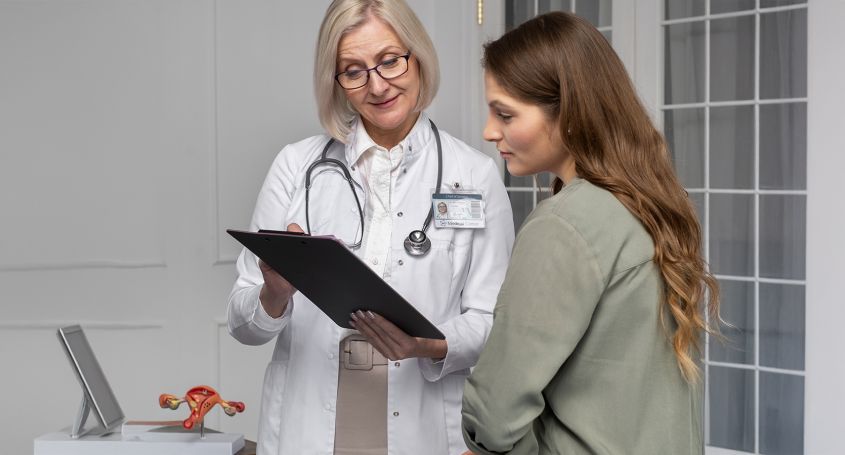
Treatment of hyperandrogenism depends on the underlying cause and symptoms of each patient. It is very important that the treatment is personalised and supervised by a specialist in assisted reproduction and gynaecological endocrinology.
Treatment options include:
- Hormone therapy: The use of combined oral contraceptives helps regulate hormone levels and reduce symptoms of hirsutism and acne.
- Ovulation inducers: such as clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins, in case of associated infertility.
- Antiandrogens: Drugs such as spironolactone or flutamide block the effects of androgens on tissues.
- Improve lifestyle: Weight loss, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce androgen production.
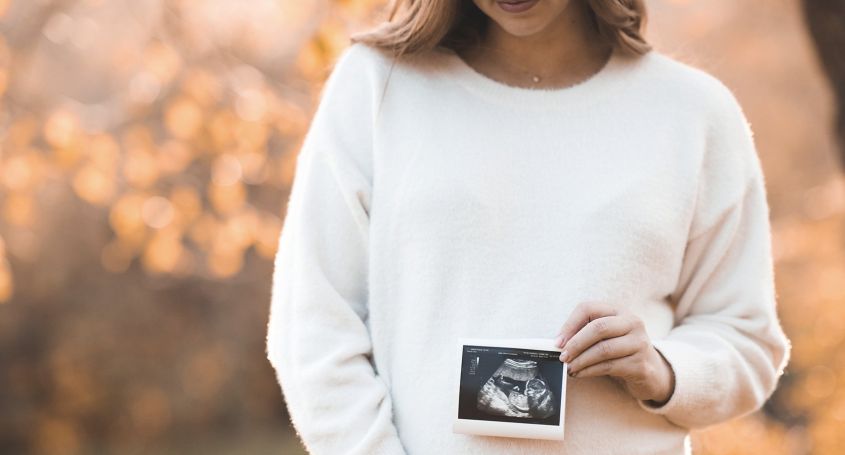
Hyperandrogenism can significantly affect female fertility. However, proper diagnosis and individualized treatment can improve ovarian function and increase the chances of achieving pregnancy.
Dr. Cristina Guix
Gynecologist specialized in fertility at Barcelona IVF