Long blastocyst culture is a widely used technique in in vitro fertilization (IVF). But what exactly is the blastocyst and how is it classified? To find out, read on!
What is the blastocyst?
The blastocyst is a stage of the embryo's development prior to its implantation in the uterus. At this stage, the embryo already has a complex cell structure made up of approximately 200 cells.
Long culture to blastocyst
Long culture to blastocyst consists of keeping the embryos obtained by IVF in an incubator until day 5 or 6 of their development, which is when they reach the blastocyst stage.
This is important because, in a natural pregnancy, the embryo reaches the uterus in the blastocyst stage after passing through the fallopian tube. Therefore, it is considered the ideal transfer stage.
Classification of the blastocyst
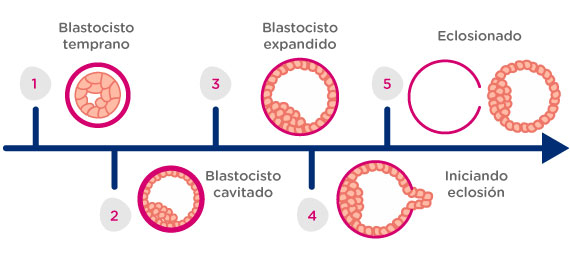
To classify blastocysts according to their degree of expansion, a morphological assessment of each stage must be performed:
- Grade 1 or early blastocyst (BT) the blastocele begins to visualize.
- Grade 2 or cavitated blastocyst (BC) it is already possible to distinguish the trophectoderm and the MCI (inner cell mass).
- Grade 3 or expanded blastocyst (BE) the blastocyst has increased in size and the layer that covers it, the zona pellucida, is thinner.
- Grade 4 or blastocyst initiating hatching (BHi) the blastocyst begins to emerge from the zona pellucida.
- Grade 5 or hatched blastocyst (BH) the blastocyst has already left the zona pellucida completely.
For whom is long blastocyst culture indicated?
This type of culture is recommended for all In Vitro Fertilization and Egg Donation cycles but especially in:
- IVF cycles in which there are a high number of embryos of good embryo quality on the 3rd day of development.
- Patients who have undergone a preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD).
- Elderly patients.
- Cases in which, for medical or other reasons, multiple pregnancies should be especially avoided.
- To optimize vitrification cycles (if you wait for the blastocyst stage to freeze the embryos, only the best ones will be frozen).
- Patients who have suffered repeated miscarriages.
- Patients in whom there have been repeated implantation failures.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of this technique?
Long blastocyst culture offers certain advantages:
- Increases implantation rate due to better embryo selection.
- It allows for better synchronization between embryo development and endometrial receptivity.
- It decreases the risk of multiple gestation (since a single embryo transfer is performed), without worsening pregnancy rates.
Even so, it also has certain limitations:
- A considerable number of embryos are blocked before reaching the blastocyst stage. This means that there is a certain risk that, on the day of the transfer, there will be no embryo to transfer. However, if the embryo has reached a blastocyst, it has a much higher chance of giving rise to a pregnancy.
Therefore, it is important to carry out a joint analysis of all the factors and thus carry out the technique that best suits each case. At Barcelona IVF we have highly qualified professionals who will advise you and make sure that the option chosen is the optimal one for you.