Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women. It is estimated that one in eight women is likely to develop it and, although it usually appears between the ages of 35 and 80, the age range with the highest incidence is between 45 and 65. The incidence of breast cancer has been growing steadily over the last few decades. This is due to multiple factors including improvements in early detection and increased life expectancy, but also increased obesity, tobacco and alcohol consumption or pollution.
Despite the increased incidence of breast cancer, mortality has decreased in recent years. This has been made possible by improvements in diagnosis and treatment, which have had a positive impact on the life expectancy and survival rate of breast cancer patients, giving reason for hope.
Advances in diagnosis and treatment
The implementation of advanced technology in screening tests such as mammography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging has made it possible to identify breast cancer earlier and more accurately, improving the prognosis of patients.
Likewise, improvements in surgical techniques, targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy have contributed to improving patient survival, reducing side effects, and delaying the start of chemotherapy, with a consequent improvement in quality of life. In addition, a better understanding of the three main types of breast cancer, such as HER2-positive, triple negative and luminal, has enabled the development of biomarkers and specific therapies that allow progress towards precision medicine.
Importance of early detection
Although there have been great advances in treatments, the prognosis of the disease depends largely on the extent of the disease at the time of diagnosis. Early detection of breast cancer is of great importance to increase the chances of cure by allowing treatment to be initiated at a less advanced stage of the disease and to opt for less aggressive treatment options.
Thanks to screening programs, about 90% of breast cancer cases are detected at an early and potentially curable stage. Mammograms are the standard way of detecting breast cancer. In the general population it is advisable to have a mammogram every 2 years between the ages of 50 and 69, but for women at higher risk due to, for example, family history, it is advisable to start screening at an earlier age.
Fertility preservation
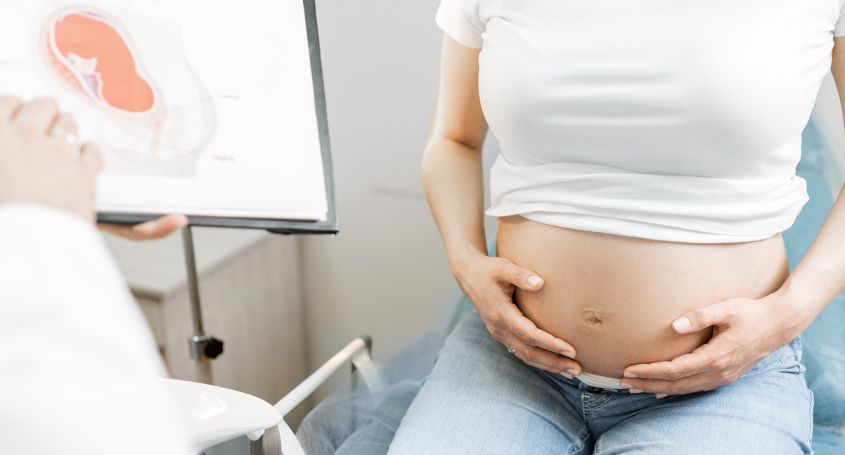
A diagnosis of cancer, including breast cancer, in women of reproductive age may raise additional concerns, as cancer treatments such as chemotherapy can affect fertility. For this reason, fertility preservation through egg or embryo cryopreservation may be recommended prior to cancer treatment.
These techniques allow patients to conserve their reproductive capacity and become mothers once the cancer has been overcome. At Barcelona IVF we are committed to providing support and solutions so that women battling breast cancer can fulfil their dream of becoming mothers in the future.