The retroverted uterus, the inverted uterus or the tilted uterus is a variant in the position of the uterus inside the pelvis. According to the Spanish Gynecological Association, approximately 20% of the female population has an inverted or retroverted uterus. But does this affect you when getting pregnant? And once you're pregnant? See below.
What is the normal position of the uterus?
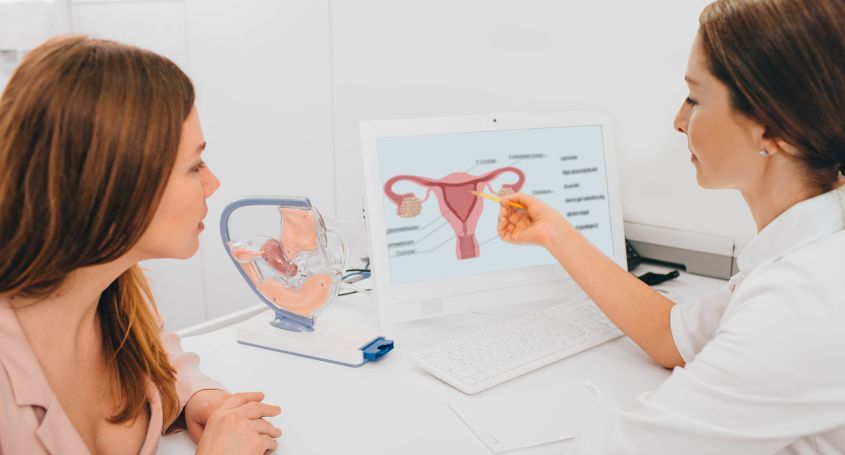
The uterus is an organ located in the pelvis and has ligaments that keep it in a central position. The position of the uterus is not fixed, but has a certain mobility.
Usually the uterus is inclined forward (in anteversion) but sometimes it can point towards the spinal column and even press against the rectum (uterus in retro).
There are many alternative ways of referring to an inclined uterus. However, all terms mean that the uterus is tilted back towards the back of the pelvis. The main ones are:
• Anteversion: is the normal or physiological position.
• Anteflexion: the uterus falls or tilts forward.
• Retroflection: the uterus folds back.
• Retroversion: the uterus falls or tilts backwards.
• Retroposition: the uterus is displaced backwards within the lower pelvis.
Causes
The inverted uterus can have a primary cause, when a girl is born with the uterus in this anatomical position or a secondary cause due to an abnormality which appears in the pelvis, for example, in cases of fibroids or adhesions (scar tissue in the pelvis). The healing of adhesions as a result of endometriosis or fibroids can cause the uterus to move. Certain gynecological conditions, such as pelvic inflammatory disease can also cause retroversion of the uterus.
Sometimes it can also be reversed due to pregnancy, but it is normal for this organ to return to normal after 10 or 12 weeks of gestation (as a result of the weight of the fetus).
Labour can also tilt the uterus forward or backward. In most cases, the uterus returns to an advanced position after delivery.
What are the symptoms?
Many women have this anatomical deviation, but many are not even aware of it, as they have no symptoms. However, the main ones are:
- Frequent pain during sexual relations due to the impact of the penis against the cervix.
- Pain in the lumbar or pelvic region at the time of premenstrual syndrome or more intense menstrual symptoms.
- Back pain during coitus.• Urinary incontinence or urine retention if the cervix presses against the bladder and the urethra, preventing the exit of urine.
- Urinary tract infections.
- Difficulty using tampons.
- Bowel movement pain due to the pressure exerted by the uterus on the rectum.
- Chronic constipation due to the same reason as above.
- Soft stools or constipation just before or during the period, because at these times the uterus can become twice as large, weighing between 120 and 300 grams, which means that the rectum has to bear much more weight.If symptoms occur, it is best to see a gynecologist. Using a general ultrasound, a pelvic examination, the gynecologist can detect the position of the uterus.
Inverted uterus: is it possible to achieve pregnancy?
Yes, it is possible to achieve pregnancy, since fertility is not affected by the inverted uterus. The upside down uterus does not interfere with the sperm’s ability to reach the egg. Once conception occurs and the fetus grows, it is likely that the uterus will correct the deviation and go back to its normal position.
However, we must bear in mind that there are other factors related to retroversion that could cause problems when conceiving, such as endometriosis, where the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus grows outside of it, for example in the ovaries, intestines, rectum, bladder, or lining of the pelvic area.
Other related diseases such as some pelvic inflammation or certain tumors could also cause problems with conception.
Even so, there are no difficulties at the time of conception and most women can achieve pregnancy and have a normal delivery.
Treatments
In general, this deviation does not usually need any type of treatment. But as it is a complex situation and can have different consequences, the specialist has to carefully monitor each case and decide on the steps to follow. For example, underlying diseases such as endometriosis or adhesions will require surgery in some cases if they produce any type of symptoms.
If you are currently aiming for pregnancy without success and you think this may be your problem, get in touch with us and we will offer you the most appropriate treatment for you.