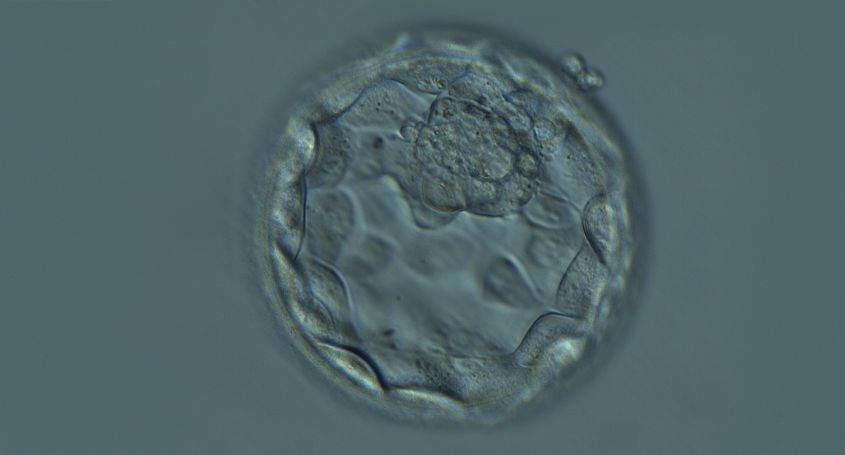
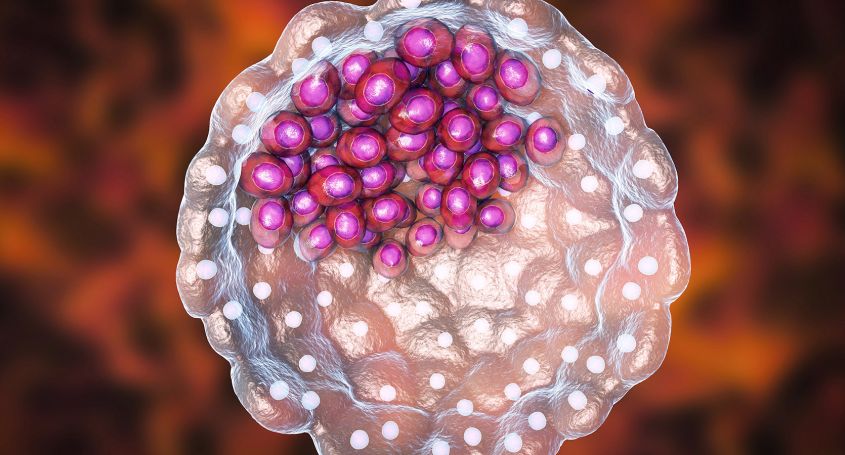
Embryo implantation is one of the most important steps during assisted reproduction treatments. However, even when an embryo with the right chromosomal endowment, known as a euploid blastocyst, is selected, implantation may not be successful.
There are additional factors beyond the genetic quality of the embryo that influence the implantation process.
Endometrial quality and receptivity
The endometrium is the inner layer of the uterus where implantation and embryo development take place. In order for the embryo to implant successfully, the endometrium must be in optimal condition to receive it. During the period of maximum receptivity, known as the "window of implantation", the endometrium undergoes structural and molecular changes that facilitate embryo attachment.
Hormonal imbalances, structural abnormalities or an abnormal hormonal response can affect endometrial receptivity and prevent implantation of even good quality embryos.
For successful implantation to occur, there must be precise synchronisation between embryo development and endometrial preparation. In cases of repeated implantation failure s with euploid blastocysts, diagnostic tests such as the ERA (Endometrial Receptivity Array) test, which measures the expression of genes associated with endometrial receptivity, can be useful to establish the window of implantation precisely.
Immune response and uterine microbiota
The maternal immune system plays a fundamental role during embryo implantation, as it must tolerate the embryo and, at the same time, protect the organism from possible pathogens. An imbalance in the immune response can lead to rejection of the embryo.
On the other hand, the uterine microbiota, composed of microorganisms present in the uterus, influences endometrial health. An altered composition of this microbiota, known as dysbiosis, has been associated with implantation failure and gestational loss.
In these cases, EMMA (Endometrial Microbiome Metagenomic Analysis), which analyses the bacterial composition of the endometrium, and ALICE (Analysis of Infectious Chronic Endometritis), which detects chronic infections of the endometrium, can help identify imbalances and infections. This allows assisted reproduction specialists to prescribe specific treatments before starting the IVF process.
Embryo selection and preparation
Although genetic evaluation is very important, morphological and developmental aspects of the embryo must also be accurately assessed. Therefore, the role of the embryologist is fundamental both in the selection of embryos with the greatest implantation potential and in the preparation of the appropriate environment to favour implantation.
In addition, innovative techniques such as assisted hatching or the use of advanced tools for embryo selection, such as iDAScore technology, contribute to improve implantation rates.
Importance of a comprehensive approach to fertility treatment
To maximise the likelihood of successful implantation, it is essential to adopt a comprehensive approach that addresses both embryo quality and endometrial health and preparedness. This involves a detailed assessment of hormonal, immunological and microbiological factors, as well as the implementation of personalised strategies based on the specific needs of each patient.
The selection of an euploid blastocyst by preimplantation genetic diagnosis is a major advance in assisted reproductive treatments. However, successful implantation depends on multiple factors. A comprehensive vision of the process and personalised care are key to improving pregnancy rates during fertility treatment.
Dr. Cristina Guix
Fertility gynaecologist in Barcelona IVF