In assisted reproduction there is the possibility of carrying out genetic tests to minimise the risk of transmission of genetic diseases. Have you heard of genetic matching and pre-implantation genetic diagnosis? We explain these tests below.
What genetic tests are there?
There are mainly 2 types of tests that are carried out in the genetics laboratories of assisted reproduction clinic s: genetic compatibility testing, also known as genetic matching, and pre-implantation genetic diagnosis.
What is genetic matching?
Most people are carriers of some hereditary recessive disease. This means that if the partner also has this mutation in his or her genes, the risk of the partner's son or daughter having the disease or being a carrier of it increases. In order to avoid this, there is a genetic compatibility test that can detect mutations in genes that may be related to this type of disease.
When is genetic matching indicated and how is it performed?
This test is recommended for donors and optional for couples undergoing assisted reproduction treatments. In addition, it only requires a blood test and a 2-3 week wait for the result.
What happens if incompatibility is found between the partners?
In cases of IVF with the couple, it is possible to resort to pre-implantation genetic diagnosis of the embryos to rule out the disease for which both are carriers or to the use of a donor.
In the case of egg donation , if the couple is not compatible with the donor, the donor is changed to ensure genetic matching.
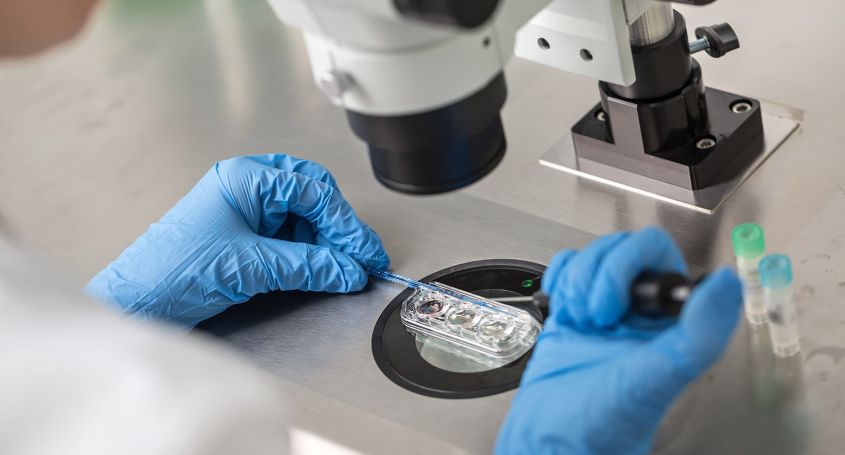
Preimplantational genetic diagnosis (PGT)
The PGT or preimplantational genetic test (PGT) is a test that makes it possible to identify and prevent the transmission of hereditary diseases to offspring through the study of embryos. This test allows the selection of viable embryos.
In fact, the DGT comprises 3 studies:
- PGT-A (preimplantation genetic test for aneuploidy): Consists of analysing the number of chromosomes in the embryo by applying NGS marker arrays.
- PGT-SR (preimplantational genetic test for structural alterations).
- PGT-M (preimplantation genetic test for monogenic abnormalities): There are a type of diseases that are caused by mutation in a gene. These alterations are not identifiable in the karyotype study, so the structure of the DNA must be analysed in order to identify them.
How are cells obtained from PGT embryos?
Embryos are biopsied when they reach the blastocyst stage (day 5-6 of development). To perform the biopsy, a laser is used to make a hole in the zona pellucida of the embryo through which the trophectoderm cells are obtained for analysis. The result of the genetic analysis will be available after a few days, so the embryos must be frozen after the biopsy (vitrification). Once we have the genetic result, the cycle for the transfer of the normal embryos to the uterus can be scheduled.
And you, were you familiar of these tests?